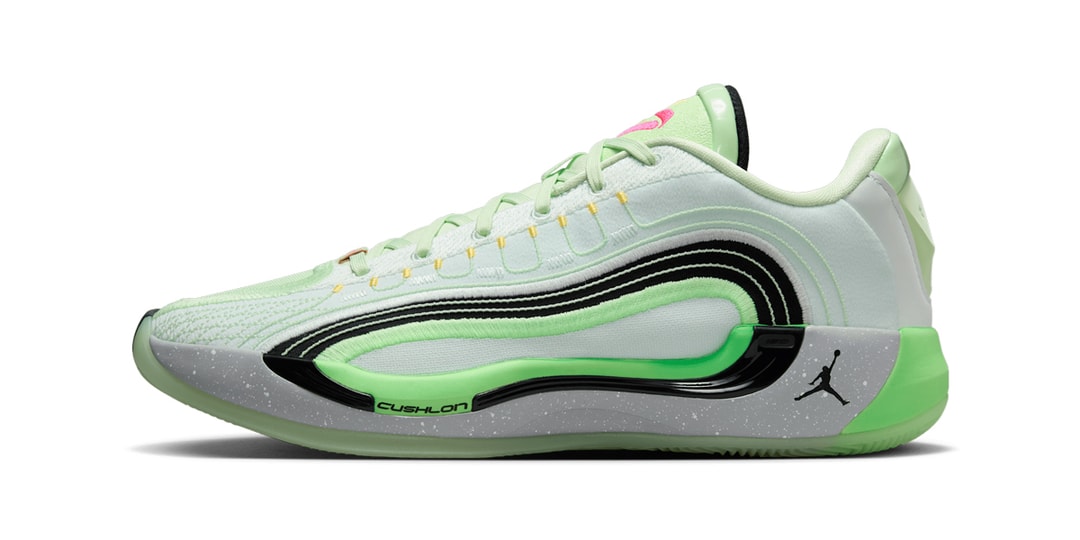
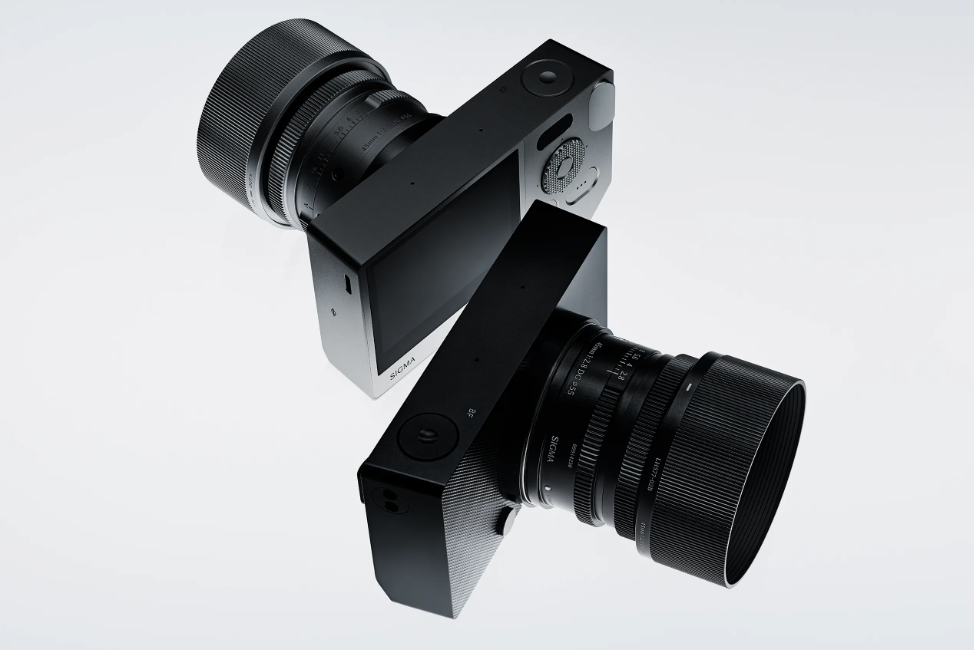
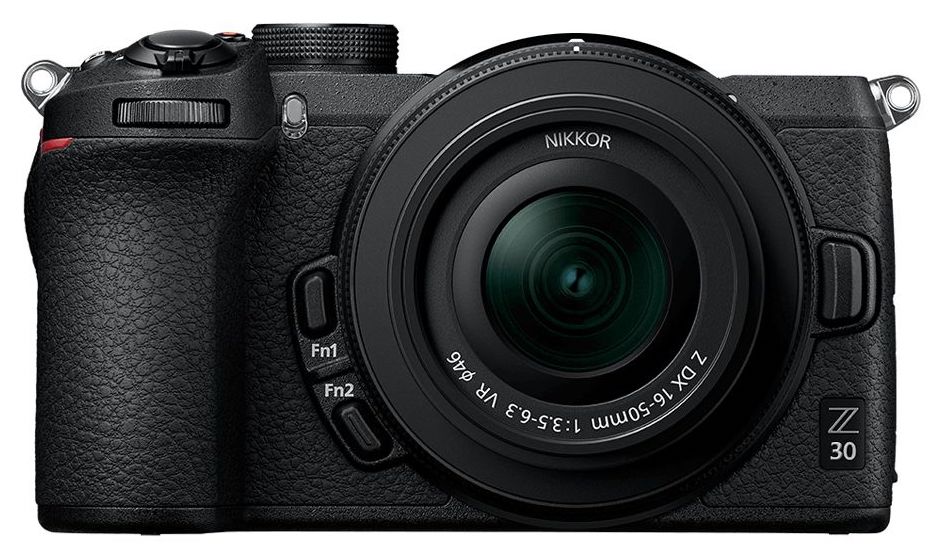
Inspiringly simple: Sigma BF review-in-progress
When you use DPReview links to buy products, the site may earn a commission. Sample galleryThis widget is not optimized for RSS feed readers. Please open this article's permalink in a browser to view this content. Product photos: Richard Butler The Sigma BF is a minimalist 24MP full-frame mirrorless camera that offers distinctive design and an unconventional user interface. Key specifications 24MP full-frame CMOS sensor Phase detection AF with human and animal detection No mechanical shutter 3.2" 2.1M dot rear touchscreen Pressure-sensitive buttons with haptic feedback 6K video up to 30p, 4K up to 30p 1080 up to 120p Leica L-Log profile Zebras and False Color exposure displays 230GB of internal memory 10Gbps USB-C port, external mic compatible The Sigma BF is available in Black or Silver at a cost of $2000. Sigma has also made versions of all its i-series primes to match the silver version of the camera. Buy now:$1999 at Amazon.comBuy at B&H Photo Index: What is it? Body and controls Initial impressions Sample gallery Specifications What is it? The Sigma BF is explicitly not trying to be a do-everything, Swiss Army Knife of a camera. Sony's a7C II already exists, bringing an EVF, multiple dials, a mechanical second-curtain shutter mechanism and in-body image stabilization, for a list price just 10% higher than the BF's. But if Sigma was trying to go head-to-head with Sony in the mass market, it probably wouldn't be spending seven hours milling each camera out of blocks of aluminium, nor doing so in Japan: neither of which is the approach you take if you're primarily driven to hit a specific price point. Similarly, just looking at the specs, the BF might be mistaken for an unstabilized Panasonic S9 in a fancier body, but despite sharing a sensor, the two cameras couldn't be more different. Instead Sigma explicitly says the BF is designed for 'everyday' photography. An elegant object designed to be carried with you, rather than a utilitarian device you take when you're taking photos. It's absolutely not optimized for rapid operation, it's not teeming with clever features. Instead it includes only the bare essentials for photography (or, arguably, slightly less than that, given its lack of mechanical shutter). Think of it like a Moleskine notebook: in many respects it's not as practical for taking notes and recording ideas as the smartphone you're already carrying, but the very process of carrying it with you acts as a prompt to look at the world and capture the thoughts you were having. The BF is trying to do the same. It's the difference between a camera that you'd grab when you want to go and take photos of something, vs a tool that encourages you to look for things to photograph. Body and controls User interface The best way to understand the BF is to note the dedicated settings display towards the top right-hand corner of the camera. This displays one of ten parameters: Drive mode File format Aspect ratio Focus mode White balance Shutter speed Aperture value Exp comp. ISO Color mode These are also the ten parameters that appear on the main screen if you press the center button on the back of the camera, in the pattern shown in the table above. You can navigate between them by pressing the cardinal points on the rear dial, then scroll the dial to change the current setting. Pressing the center button lets you see and edit the camera's core ten parameters, but chosen setting is also shown in the dedicated settings display to the top right of the screen. In this instance the aperture value is shown in dark grey because it's being controlled from the lens. But you don't have to press the center button and bring them up on the main screen: once you've learned their relative positions (and chances are it's the ones in the bottom row you'll change regularly), you can navigate around them just using the settings display. And, for me, that's the key to understanding the BF: it's designed so that the core settings can be adjusted without looking at the main screen. You can set the camera to show all the settings on the main screen, In keeping with this idea, the touchscreen is almost solely used for positioning the AF point or selecting a subject to track: even if you summon-up the settings on the main screen, you can't tap to change settings, just choose what to focus on. Exposure modes The BF has no mode dial, so exposure mode is set by selecting which parameters you want to be controlled by the camera. This is done via the main screen. Press the center button to bring up the settings then press it again to edit them, and the ISO, aperture value and shutter speed indicators show 'Auto' options above them, letting you engage and disengage automated control of each parameter. Any of the exposure parameters that can't be changed by spinning the dial, either because they're set to Auto or because aperture value is being set by an aperture ring, is rendered in

 |
Product photos: Richard Butler
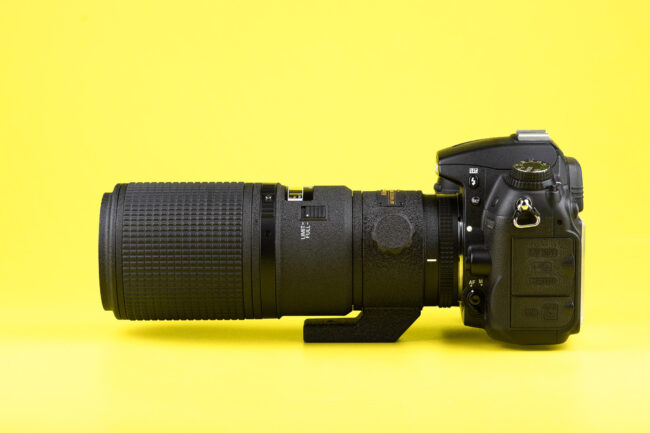
The Sigma BF is a minimalist 24MP full-frame mirrorless camera that offers distinctive design and an unconventional user interface.
Key specifications
- 24MP full-frame CMOS sensor
- Phase detection AF with human and animal detection
- No mechanical shutter
- 3.2" 2.1M dot rear touchscreen
- Pressure-sensitive buttons with haptic feedback
- 6K video up to 30p, 4K up to 30p
- 1080 up to 120p
- Leica L-Log profile
- Zebras and False Color exposure displays
- 230GB of internal memory
- 10Gbps USB-C port, external mic compatible
The Sigma BF is available in Black or Silver at a cost of $2000. Sigma has also made versions of all its i-series primes to match the silver version of the camera.
Index:
What is it?
 |
The Sigma BF is explicitly not trying to be a do-everything, Swiss Army Knife of a camera. Sony's a7C II already exists, bringing an EVF, multiple dials, a mechanical second-curtain shutter mechanism and in-body image stabilization, for a list price just 10% higher than the BF's.
But if Sigma was trying to go head-to-head with Sony in the mass market, it probably wouldn't be spending seven hours milling each camera out of blocks of aluminium, nor doing so in Japan: neither of which is the approach you take if you're primarily driven to hit a specific price point.
Similarly, just looking at the specs, the BF might be mistaken for an unstabilized Panasonic S9 in a fancier body, but despite sharing a sensor, the two cameras couldn't be more different.
Instead Sigma explicitly says the BF is designed for 'everyday' photography. An elegant object designed to be carried with you, rather than a utilitarian device you take when you're taking photos. It's absolutely not optimized for rapid operation, it's not teeming with clever features. Instead it includes only the bare essentials for photography (or, arguably, slightly less than that, given its lack of mechanical shutter).
 |
Think of it like a Moleskine notebook: in many respects it's not as practical for taking notes and recording ideas as the smartphone you're already carrying, but the very process of carrying it with you acts as a prompt to look at the world and capture the thoughts you were having. The BF is trying to do the same.
It's the difference between a camera that you'd grab when you want to go and take photos of something, vs a tool that encourages you to look for things to photograph.
Body and controls
 |
User interface
The best way to understand the BF is to note the dedicated settings display towards the top right-hand corner of the camera. This displays one of ten parameters:
| Drive mode | File format | Aspect ratio | Focus mode | White balance |
| Shutter speed | Aperture value | Exp comp. | ISO | Color mode |
These are also the ten parameters that appear on the main screen if you press the center button on the back of the camera, in the pattern shown in the table above.
You can navigate between them by pressing the cardinal points on the rear dial, then scroll the dial to change the current setting.
But you don't have to press the center button and bring them up on the main screen: once you've learned their relative positions (and chances are it's the ones in the bottom row you'll change regularly), you can navigate around them just using the settings display. And, for me, that's the key to understanding the BF: it's designed so that the core settings can be adjusted without looking at the main screen. You can set the camera to show all the settings on the main screen,
In keeping with this idea, the touchscreen is almost solely used for positioning the AF point or selecting a subject to track: even if you summon-up the settings on the main screen, you can't tap to change settings, just choose what to focus on.
Exposure modes
The BF has no mode dial, so exposure mode is set by selecting which parameters you want to be controlled by the camera. This is done via the main screen. Press the center button to bring up the settings then press it again to edit them, and the ISO, aperture value and shutter speed indicators show 'Auto' options above them, letting you engage and disengage automated control of each parameter.
Any of the exposure parameters that can't be changed by spinning the dial, either because they're set to Auto or because aperture value is being set by an aperture ring, is rendered in darker grey, both in the settings display and on the main screen display.
Other settings
Another ten settings, six of which relate to how much detail appears on the main screen (exposure parameters, guides, virtual horizon, etc), can be accessed by pressing the 'three dots' settings button. At the bottom of this settings menu is the word 'System' which gives you access to a ten-option-long list of fundamental camera settings, including firmware information, copyright information, menu language and date/time.
That's the extent of the BF's interface: ten top-level parameters, ten settings and ten menu options. But what this doesn't fully convey is the degree to which it's a camera in which Shutter speed, Aperture value, Exposure compensation and ISO can all be set using just the settings display, leaving the monitor solely for focus and composition.
Handling
 |
The BF is a very solid-feeling camera, as you might expect from something hewn from a solid block of metal. The body itself is relatively light but the weight adds up as soon as you mount a lens of any appreciable size on it.
Despite it's minimalist appearance, it's quite easy to hold. The textured front-plate and raised thumb rest at the back mean you can get a pretty solid grip on the camera, and you can cradle the weight of the lens in your left hand if you're working with anything larger than one of the compact primes offered by Sigma or Panasonic.
However, we found that it was common for our ring finger to wrap around to the base of the camera as we held it, which quickly makes apparent how sharply angled the edge of the BF is. It's not hard to imagine users adding a little tape to the lower edge of the camera or being tempted to chamfer the edge with a fine file, once they come to live with the camera.
I've primarily used it with the Sigma 35mm F2 prime and the Panasonic 20-60mm F3.5-5.6 lenses, both of which are small and light enough that it's been comfortable to use.
Battery
 |
The BF uses a new 11.88Wh BP-81 battery. This will power the camera to a CIPA rating of 260 shots per charge. As always, the CIPA figure will tend to under-represent how many shots you're likely to get, and we found it's the camera's propensity to show its charge percentage on its settings display that caused us to worry a little disproportionately.
Still, a rating of 260 is pretty low and means you may want to consider carrying a power bank if you plan to do more than occasional shots each day. Putting it on to charge overnight, just as you might do with your phone will probably be sufficient for everyday casual use, though.
A gentle press of the power button puts the camera into stanby mode, but the battery will continue to drain at an appreciable rate. The BF starts up from cold quickly enough that this is usually a better approach.
Initial impressions
By Richard Butler
 |
| Even the body cap is an over-engineered delight. |
The Sigma BF is one of the most unusual cameras we've ever encountered. On paper it looks like an under-specced rival to the Panasonic DC-S9 or even the Sony a7C II. Or, perhaps even a slightly re-purposed Sigma fp. But, even though it shares components and a small rectangular body, the BF is quite unlike any of these cameras.
Sigma's CEO, Kazuto Yamaki talked about completely re-thinking the camera's interface to pare it back to the fundamental things a camera needs to offer, in an attempt to make it simple to use, with the aim of making a camera for everyday use. And the more I use the BF,. the more I think I understand this intent.
The idea of a dedicated settings display, leaving the main screen as a means of composing your image and positioning the focus point is a refreshingly simple one, undermined only by the challenge of viewing a fixed LCD in bright light. The decision to display only one setting, rather than a full array of settings and icons makes it very quick to interpret and I did find it made me consider what changes I wanted to make, shot-to-shot, in a way I don't on a more conventional twin-dial camera.
This really hit home when I realised I prefer to set aperture from the camera, rather than using an aperture ring; I think the camera works best with everything controlled from the settings display, rather than trying to increase the number of control points.
Another suprise was how good the BF's autofocus appears to be. Its subject tracking is very simple to use and impressively tenatious, its eye detection works well and can be left turned on without minimal risk of the camera prioritising nearby faces ahead of a different subject you've selected.
There are distinct downsides, though, the lack of mechanical shutter not only means there's a risk of rolling shutter and that the camera can't be used with flash, it also means it's distinctly prone to banding caused by the inherent flicker of artificial lights. This can be fairly subtle at longer shutter speeds but becomes increasingly apparent in short exposures, limiting its use as an indoor camera, despite a sensor that works well in low light.
 |
|
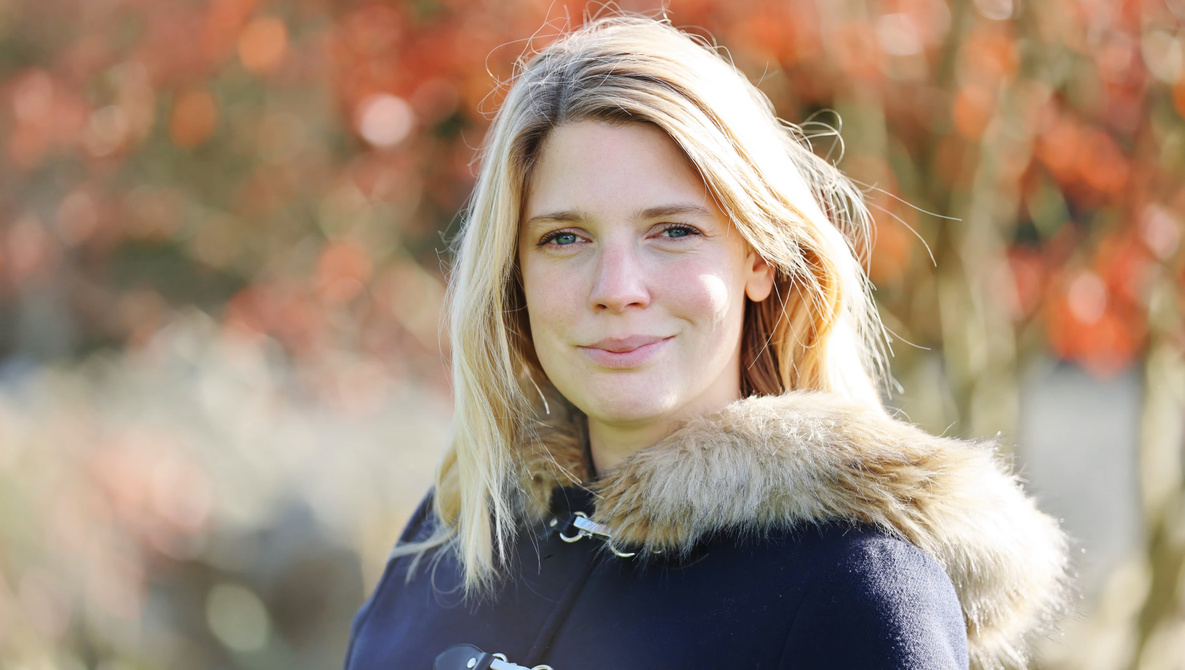
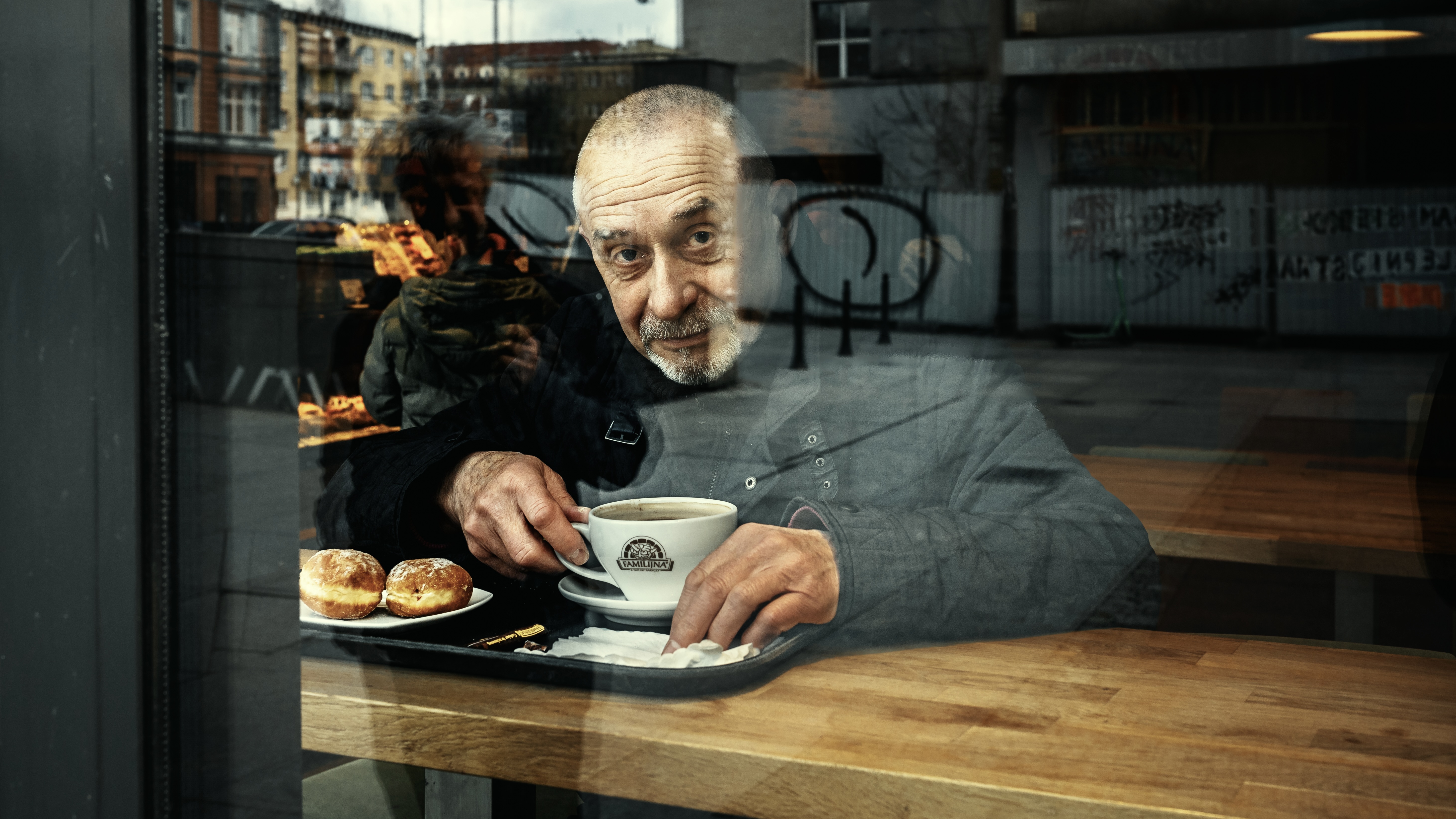
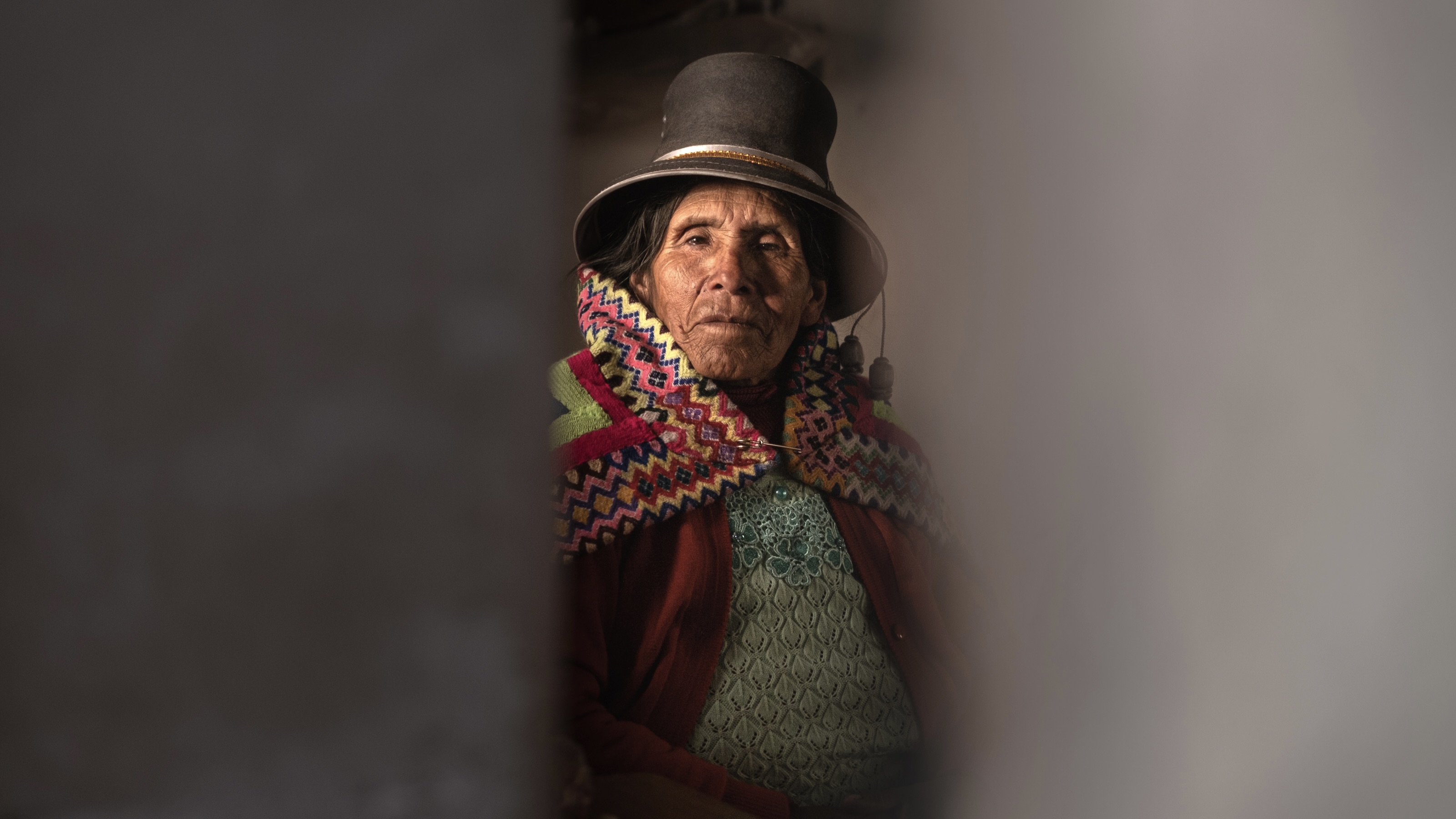
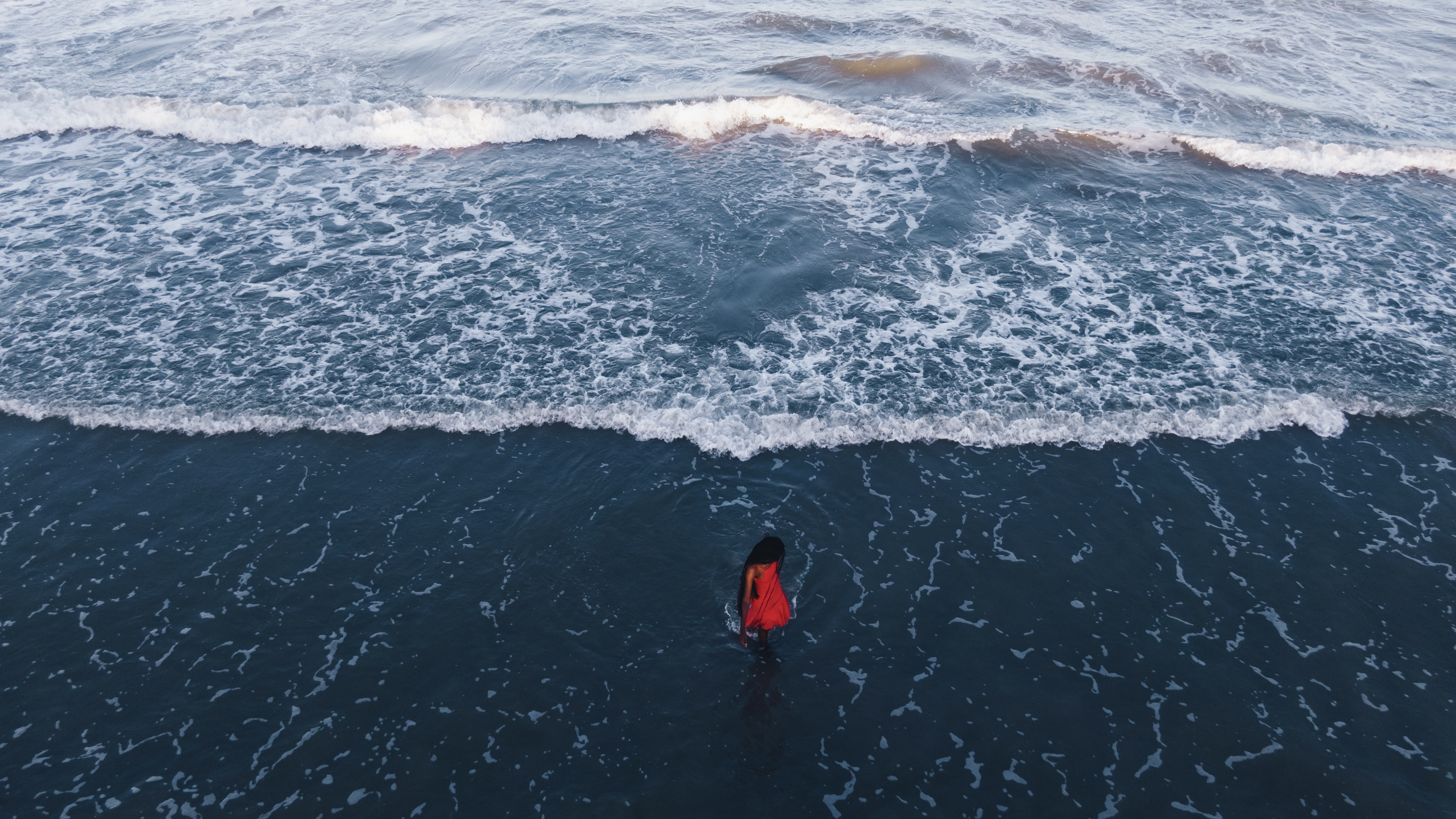
Sigma 35mm F2.0 | F4.0 | 1/500 sec | ISO 400 Photo: Richard Butler |
Sigma's sometimes quite dramatic color modes may not be to everyone's tastes, and I'm not wholly convinced by the 'Light Source Priority' auto white balance mode, that tries to maintain some of the character of the detected light source. But even when the results are unexpected, they're often interesting.
The BF's battery life is also quite short. An external charger is available, if you want to keep a second battery topped-up, but mainly it's a case of remembering to put the camera on to charge regularly, just as you might for your smartphone.
Other than a slight concern about the sharp lower front edge, I'm really looking forward to spending more time with the BF. It's not a camera that lets you respond quickly to the unexpected, instead it's one that makes you slow down and look for the photos you might otherwise not notice.






























































-PowerWash-Simulator-2-Announce-Trailer-00-00-20.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=80&format=jpg&auto=webp#)




















.jpg?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=80&format=jpg&auto=webp#)